-
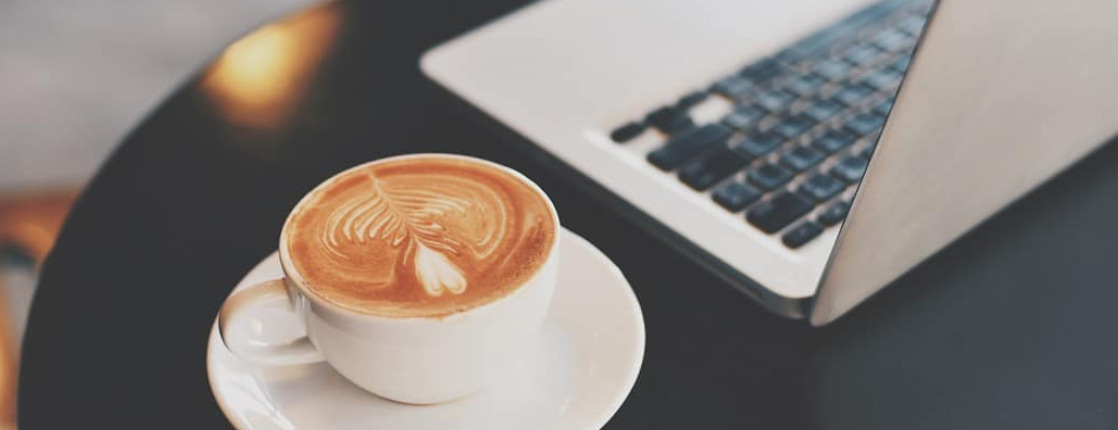
Milk Composition and Its Impact on Froth Stability: The stability of foam produced by a handheld milk frother is heavily influenced by the chemical composition of the milk, particularly its protein and fat content. Whole milk contains higher levels of fat and casein proteins, which stabilize the air bubbles formed during frothing, resulting in a creamier, denser foam that holds its structure for a longer period. Skim milk, on the other hand, has lower fat content, producing lighter foam that is prone to rapid collapse. Plant-based alternatives, such as almond, oat, or soy milk, have variable protein and fat contents, which can dramatically affect the foam’s consistency. Soy and oat milk, when fortified with proteins, produce more stable foam than almond or rice milk. Understanding the milk’s composition allows users to select the optimal type for creating long-lasting, café-quality froth with a handheld milk frother.
-
Frothing Mechanism and Whisk Design: The mechanical design of a handheld milk frother plays a crucial role in the stability of the froth it produces. High-speed motors combined with tightly wound or dual-whisk designs create smaller, uniform air bubbles, which significantly enhance foam stability by reducing coalescence and collapse over time. Frothers with lower motor speed or loosely designed whisks tend to produce larger, uneven bubbles that lack structural integrity, causing foam to dissipate quickly. The efficiency of air incorporation, turbulence generation, and whisk-to-milk contact directly affects the foam’s texture and longevity. For users seeking stable, long-lasting foam for beverages such as lattes or cappuccinos, investing in a handheld frother with high rotational speed and optimized whisk geometry ensures more reliable results and better control over foam quality.
-
Milk Temperature During Frothing: Temperature is another critical factor that impacts foam stability in a handheld milk frother. Proteins in milk denature and unfold optimally within a specific temperature range, usually between 60°C and 65°C (140°F–149°F) for hot beverages. Frothing milk that is too cold results in insufficient protein denaturation, producing weak foam that collapses rapidly. Conversely, milk that is too hot can cause proteins to over-denature or coagulate, destabilizing the foam and creating a thin, watery texture. Cold frothing for iced beverages can work effectively with specialized frothers, but even in this case, foam tends to be less dense and dissipates more quickly than hot milk foam. Maintaining precise temperature control ensures that the foam retains its structure and provides a consistent, professional appearance and mouthfeel.
-
Container Shape and Frothing Technique: The container in which milk is frothed significantly affects the distribution of air and the stability of the foam. Tall, narrow containers encourage better circulation and allow the whisk to evenly incorporate air, generating a uniform microfoam structure. Shallow or wide containers, however, often lead to uneven frothing, larger bubbles, and faster foam collapse. The technique used—such as submerging the whisk just below the surface versus deep in the milk, and moving the frother in circular or vertical motions—affects air incorporation and bubble size. Correct container selection and proper frothing technique are essential to maximize foam stability and ensure the froth maintains volume and texture long enough for practical use in beverages.
-
Comparison to Professional Espresso Machine Foam: While handheld milk frothers can create café-style froth quickly and conveniently, the foam’s stability typically does not match that produced by professional espresso machines with steam wands. Steam frothing introduces both heat and microbubbles under high pressure, producing denser, more uniform foam with excellent long-term stability. Handheld frothers rely solely on mechanical agitation, which limits microbubble uniformity and tends to produce foam that dissipates more rapidly. For hot beverages, dense foam from a handheld frother may last 3–5 minutes, whereas light foam can collapse within 1–2 minutes. Despite this limitation, using proper milk selection, frother speed, temperature, and technique can optimize foam longevity and quality for home or casual use, making handheld frothers a versatile tool for creating professional-style beverages in a domestic setting.



 English
English
 Français
Français
 Español
Español
 Deutsch
Deutsch
 日本語
日本語